What is an API?
API is the acronym for Application Programming Interface. It is a software interface that allows two applications to interact with each other without any user intervention.
API is an stands for Application Programming Interface and By definition, it can be defined as a software interface used to access data, server software or other applications Confused? Let’s understand it in layman terms, In a nutshell; An API is a software intermediary that allows two applications to talk to each other. And you can think of an API as a translator between two people who don’t speak the same language but can communicate using a go-between. For Example, when in a restaurant, you don’t ideally speak to the chef, you give your order to the waiter and waiter tells the chef what to prepare dish for your table, in this case, you can consider waiter acting as an API By nature, APIs are very versatile and can be used on.
- Web-based Systems,
- Operating Systems,
- Database Systems
- Computer Hardware.
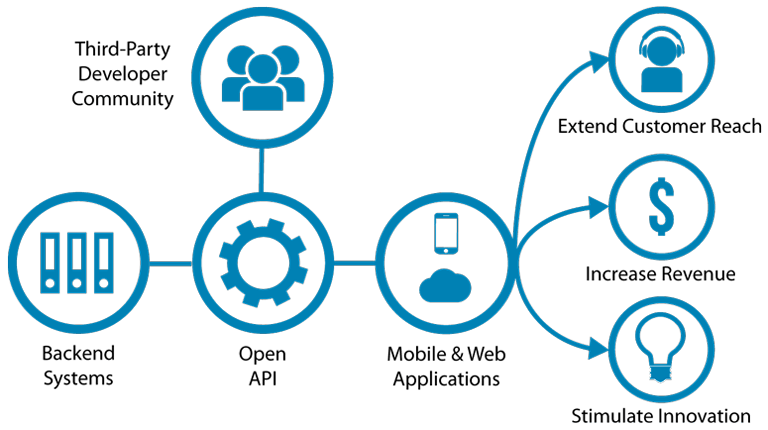
Developers use APIs to make their jobs more efficient by reusing code from before and only changing the part that is relevant to the process they want to improve. A good API makes it easier to create a program because the building blocks are in place and makes use of defined protocols to enable developers to build, connect and integrate applications quickly and at scale.
Now, let’s understand how they work
Well, an API communicate through a set of rules that define how computers, applications or machine scan talk to each other. To understand an API, let’s take an for example of you signing into Facebook from your phone, while doing this, you are telling Facebook application that you would like to access your account. Your application then makes call to an API, to retrieve your account and credentials. The API acts as a middleman between you and the Facebook’s server to let you use your account on your device. Once your credentials match, Facebook would then access this information from one of its servers and return the data to the mobile application. These types of APIs called web APIs are the most commonly used but they are limited just to the web. But there’s a lot more of them, let’s take a look at each one by one.
Types of APIs
- REST (RESTful) API.
- Simple Object Access Protocol(SOAP).
- Extensible Markup Language— Remote Procedure Calls(XML-RPC ).
- JSON-RPC
- REST (RESTful) API: stands for representational state transfer and delivers data using the light weight JSON format. Most public APIs use this because of its fast performance, dependability and ability to scale by reusing modular components without affecting the system as a whole.
- Simple Object Access Protocol(SOAP): It stands for Simple Object Access Protocol is a little more complex then REST because it requires more upfront about how it sends its messages. This API has been around since the late 1990s and uses XML to transfer data. It requires strict rules and advanced security that require more bandwidth. This protocol does not have the ability to cache, and has strict communication and need sever piece of information about an interaction before any calls are even thought of to be processed.
- Extensible Markup Language: Remote Procedure Calls(XML-RPC ): Stands for Extensible Markup Language— Remote Procedure Calls. This uses a specific XML format and in this, a client performs a RPC by sending an HTTP request to a server that implements XML-RPC and receives the HTTP response.
- JSON-RPC: — Is very similar to XML-RPC in that they work the same way except that this protocol uses JSON instead of XML format. The client is typically software that calls on a single method of a remote system.